Healthy Crops lead to higher yields
Crop Health Monitoring
DroneHive’s Crop Health Monitoring Package harnesses the power of the DJI Mavic 3M’s multispectral sensors to give you a clear, data‑driven view of plant health across your fields. By capturing light beyond the visible spectrum—green, red, red‑edge, and near‑infrared—the system reveals subtle variations in crop vigor, moisture stress, and nutrient deficiencies before they become obvious.
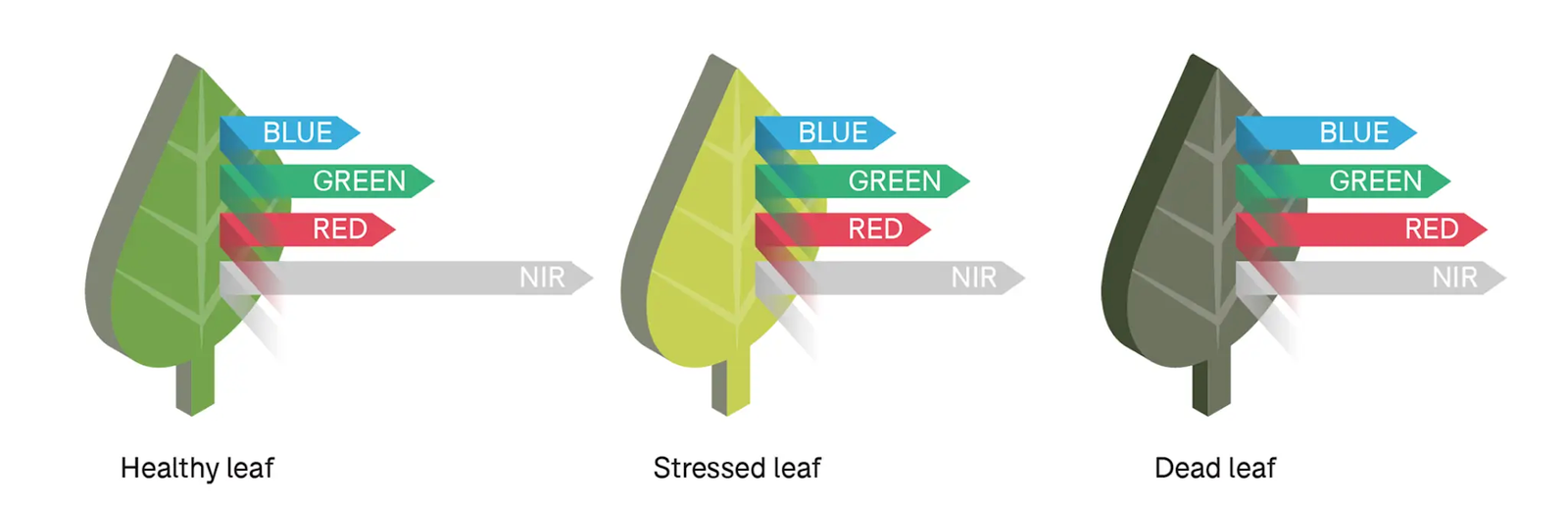
How Multispectral Technology works?
Multispectral mapping involves mounting specialized cameras on a drone to capture separate images at specific wavelengths. During a flight, the Mavic 3M synchronizes its four band‑specific sensors—green (560 ± 16 nm), red (650 ± 16 nm), red‑edge (730 ± 16 nm), and near‑infrared (860 ± 26 nm)—alongside a standard RGB camera.
NDVI
Measures the “greenness” of plants by comparing near‑infrared and red light reflectance. A high NDVI value means dense, healthy foliage; low values indicate sparse or stressed vegetation.
- Gauge overall plant vigor in early growth stages
- Identify areas with uneven water distribution
- Estimate nutrient levels when moisture is sufficient
NDRE
Similar to NDVI but uses the red‑edge band instead of red light, so it penetrates deeper into dense canopies. NDRE is especially valuable later in the season, when leaves are thicker and NDVI begins to plateau.
- Track chlorophyll levels in mature crops
- Spot stress under heavy foliage
- Guide nitrogen or fertilizer applications
OSAVI
Adjusts the basic NDVI formula to account for bare soil reflectance, making it more reliable when plants are sparse or ground visibility is high. OSAVI helps isolate true plant signals from background soil.
- Differentiate vegetation from exposed soil during early growth
- Improve accuracy in fields with mixed plant cover
- Serve as a foundation for more complex structural indices
GNDVI
Replaces the red band in NDVI with green light, offering a more stable measure under dense canopies or later growth stages. GNDVI often correlates closely with water and nitrogen uptake in crops.
- Monitor water stress and irrigation needs
- Assess nitrogen absorption in leafy crops
- Validate canopy density in advanced growth phases
NDVI
Measures the “greenness” of plants by comparing near‑infrared and red light reflectance. A high NDVI value means dense, healthy foliage; low values indicate sparse or stressed vegetation.
- Gauge overall plant vigor in early growth stages
- Identify areas with uneven water distribution
- Estimate nutrient levels when moisture is sufficient
NDRE
Similar to NDVI but uses the red‑edge band instead of red light, so it penetrates deeper into dense canopies. NDRE is especially valuable later in the season, when leaves are thicker and NDVI begins to plateau.
- Track chlorophyll levels in mature crops
- Spot stress under heavy foliage
- Guide nitrogen or fertilizer applications
OSAVI
Adjusts the basic NDVI formula to account for bare soil reflectance, making it more reliable when plants are sparse or ground visibility is high. OSAVI helps isolate true plant signals from background soil.
- Differentiate vegetation from exposed soil during early growth
- Improve accuracy in fields with mixed plant cover
- Serve as a foundation for more complex structural indices
GNDVI
Replaces the red band in NDVI with green light, offering a more stable measure under dense canopies or later growth stages. GNDVI often correlates closely with water and nitrogen uptake in crops.
- Monitor water stress and irrigation needs
- Assess nitrogen absorption in leafy crops
- Validate canopy density in advanced growth phases
Healthy Crops lead to higher yields
Benefits you’ll see
Early Problem Detection
Spot nutrient deficiencies, pests, or irrigation issues before they spread.
Targeted Treatments
Apply water, fertilizer, or pesticides exactly where they’re needed, saving costs and reducing waste.
Yield Optimization
Use data‑driven insights to make informed decisions that boost crop performance.
Historical Comparisons
Track changes over time to validate interventions and plan future plantings.



